If odds are stated as an A to B chance of winning then the probability of winning is given as P W = A / (A B) while the probability of losing is given as P L = B / (A B) For example, you win a game if you pull an ace out of a full deck of 52 cards Pulling any other card you loseObtain the logodds for a given probability by taking the natural logarithm of the odds, eg,log(025)= or using theqlogisfunction on the probability value, eg,qlogis(02)= Lastly, using the American methodology, Australia's odds to win the 15 ICC Cricket World Cup is 250 Therefore, the implied probability equals 7143% ( 2

Logistic Regression Calculating A Probability
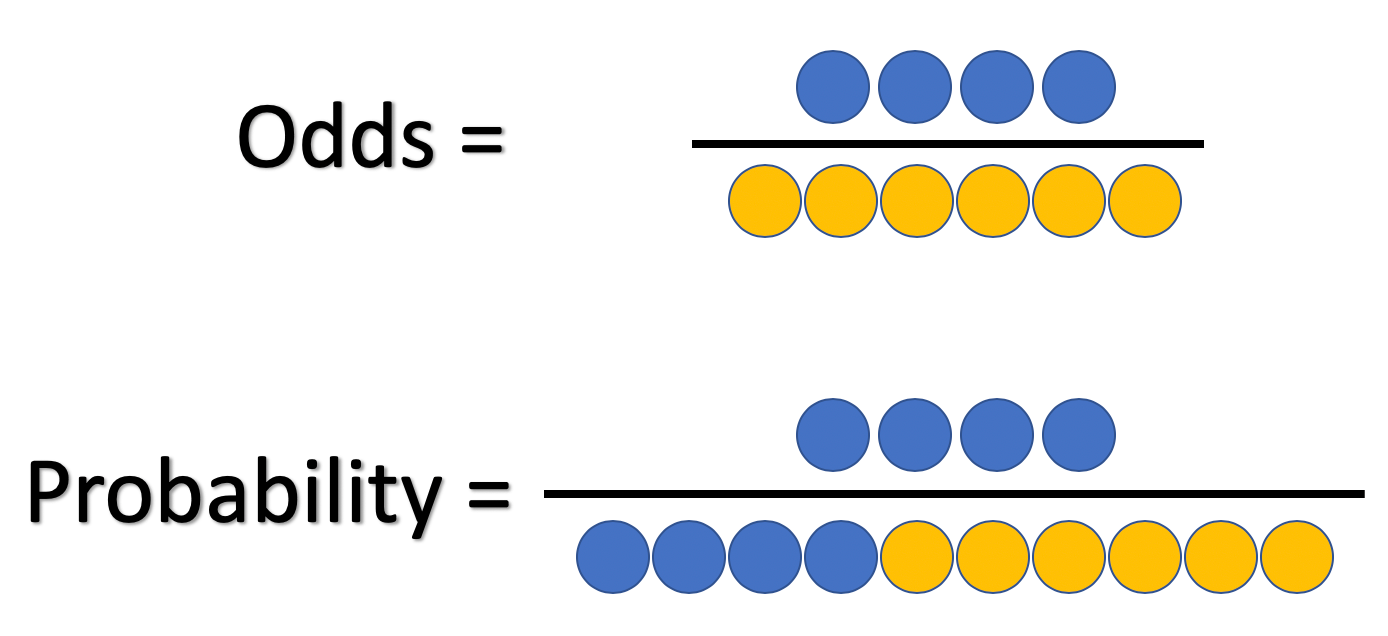
Odds against probability formula
Odds against probability formula- To calculate probability given the odds Probability = odds/1 odds To go in the other direction from odds to probability Divide the odds by 1 odds In this example, (1/4) / (11/4) = (1/4) / (5/4) = 1/5, the probability Let's apply the same formula to the odds for tails (1 / 15) x 100 = 6667% The actual probability of a wager on tails winning is also 50%, which is LESS than the implied probability of the associated odds Therefore, a wager on tails at 15 offers negative value




Odds And Probability
Odds the ratio of the probability that an event will occur versus the probability that the event will not occur, or probability / (1probability) For example, if you are normally on call 2 out of 7 days in a week, then the odds of you being on call on a certain day of the week is (2/7)/(5/7) = 040The odds of winning are 1/9,999 () and the probability of winning is 1/10,000 () In this case, odds and probability are essentially identical Relative Risk (RR) & Odds Ratio (OR) The difference between odds and probability is important because Relative Risk is calculated with probability and Odds Ratio is calculated with odds Odds The relationship between x and probability is not very intuitive Let's modify the above equation to find an intuitive equation Step1 Calculate the probability of not having blood sugar Step2 Where p = probability of having diabetes 1p = probability of not having diabetes You can interpret odd like below
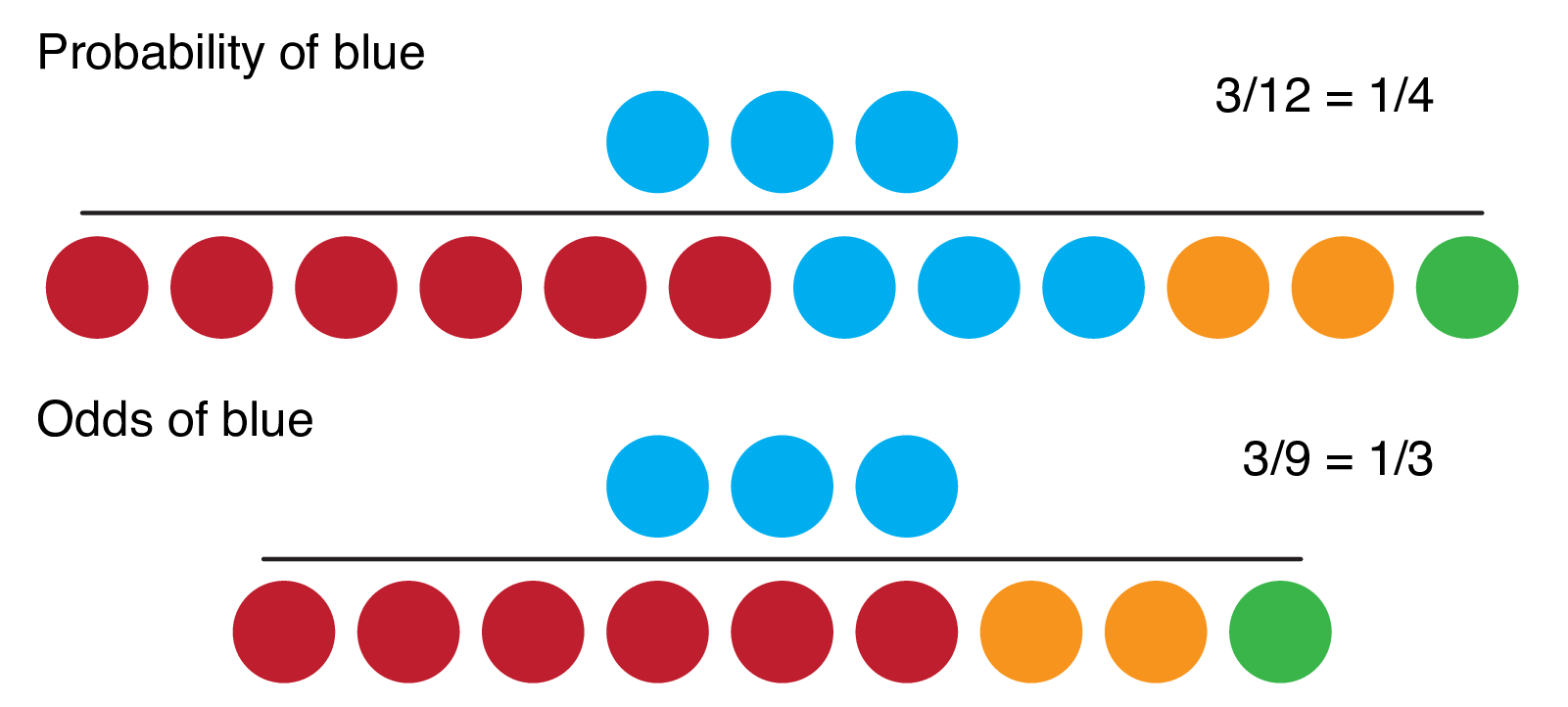
The probability of having the winning plate is 1 out of 25 Odds of winning = number of chances to win number of chances to draw other numbers Odds of winning = 124 (Read as "1 to 24") Odds of not winning = number of chances to draw other numbers number of chances to win Odds of not winning = 241 (Read as "24 to 1") The answer is the total number of outcomes Probability can be expressed as 9/30 = 3/10 = 30% the number of favorable outcomes over the number of total possible outcomes A simple formula for calculating odds from probability is O = P / (1 P) A formula for calculating probability from odds is P = O / (O 1)A fractional listing of 6/1 (sixtoone) odds would mean that you win $6 against every $1 you wager, in addition to receiving your dollar back (ie, the amount you wagered)
The Ask Dr Math forum has several entries on odds versus probability Summarizing, one way to conceptualize (nontechnically) the probability of an event is the number of ways that an event can occur divided by the total number of possible outcomes The probability of heads in a fair coin flip is 1/2 (50 percent) The pretest odds = pretest probability / (1pretest probability) As the pretest probability is the same as the prevalence of POAG in the population, the pretest odds 0025 / 0975 = 003 Posttest odds = pretest odds * LR = 003 * = 06 We now calculate posttest probability Posttest probability = posttest odds / (posttest odds1)BioEpi540W 6 Applications of Probability in Epidemiology Page 11 of 17 b Odds("comparison of two complementary (opposite) outcomes") In words, the odds of an event "E" is the chances of the event occurring in comparison to




Estimating An Odds Ratio From A Gwas Only Reporting The P Value Sean Harrison Blog




How To Calculate Odds 11 Steps With Pictures Wikihow
On the other hand, odds are a bit more complicated and represent the probability that something will occur, divided by the probability that it will not occur Think about it as though you were betting on an underdog racehorse, and your odds compare the chance of that horse winning against the other horses Probability vs Odds Real life is full of incidents with uncertainty The terms probability and odds measure one's belief in the occurrence of a future event It may confuse since both 'Odds' and 'probability' are related to the potential that event occurs However, there is a difference Probability is a broader mathematical conceptOdds The odds in favor of an event is the ratio of the number of ways the outcome can occur to the number of ways the outcome cannot occur # of ways the event CAN occur # of ways the event CANNOT occur This is actually a lot easier than probability



What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science




May The Odds Be In Your Favour Financially
This video explains how to determine odds in favor and odds against from a given probabilitySite http//mathispower4ucom Odds can be expressed as a ratio of the probability an event will happen divided by the probability an event won't happen Odds in favor of A = A / (1 A), usually simplified to lowest terms, For instance, if the probability of an event occurring is 075, then the odds for it happening are 075/025 = 3/1 = 3 to 1 for, while the probability that it doesn't occur is 1 to 3 againstOdds is a see also of probability As nouns the difference between odds and probability is that odds is the ratio of the probabilities of an event happening to that of it not happening while probability is the state of being probable;




Probability Vs Odds What S The Difference Learn It And By Z Ai Towards Data Science



9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science
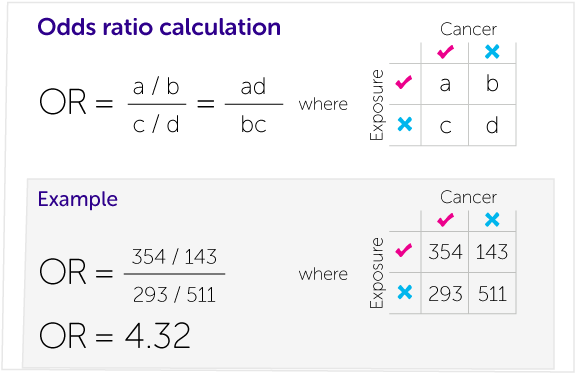
Understanding odds conversion to the percentage and implied probability behind the odds on offer is key to assessing the potential value in a particular betting market And it is just as important when assessing the value that exists with regards to specific odds on a particular outcomeFinding the odds Odds are used to describe the chance of an event occurring The odds are the ratios that compare the number of ways the event can occur with the number of ways the event cannot occurr The odds in favor the ratio of the number of ways that an outcome can occur compared to how many ways it cannot occurThe formula can also be presented as (a × d)/ (b × c) (this is called the crossproduct) The result is the same (17 × 248) = (/4216) = 371 The result of an odds ratio is interpreted as follows The patients who received standard care died 371 times more often than patients treated with the



Are You Mixing Up Odds With Probability By Keith Mcnulty Towards Data Science




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor
An odds ratio (OR) is a statistic that quantifies the strength of the association between two events, A and B The odds ratio is defined as the ratio of the odds of A in the presence of B and the odds of A in the absence of B, or equivalently (due to symmetry), the ratio of the odds of B in the presence of A and the odds of B in the absence of ATwo events are independent if and only if the OR 5 Multiply to calculate your odds of winning the jackpot To calculate the odds that you'll guess the first 5 numbers and the Powerball correctly to win the jackpot, multiply the odds that you'll guess the first 5 numbers (1 in 11,238,513) by the odds that you'll guess the Powerball correctly (1 in 26) Odds are often expressed as odds for, which in this case would be three divided by seven, which is about 43% or 043, or odds against, which would be seven divided by three, which is 233% or 233 How does odds relate to probability?



Probability Probability Vs Odds Lesson Math Statistics Showme




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1 Study Skills Research Methods College Survival
Probability theory is an interesting area of statistics concerned with the odds or chances of an event happening in a trial, eg getting a six when a dice is thrown or drawing an ace of hearts from a pack of cards To work out odds, we also need to have an understanding of permutations and combinationsA probability is always expressed as a number between 0 and 1 Odds on the other hand are expressed as the likelihood of an event occurring divided by the likelihood of it not occurring Probabilities of 0 are the same as odds of 0 If the probability is between 0 and 05, the oddsFinding Odds using Probability Probabilities for and against the event can be used as the antecedent and consequent of the ratio representing the odds for an event in place of favorable and unfavorable choices



Odds Likelihood Ratios Guide To Diagnostic Tests




Ex Determine Odds In Favor And Odds Against From A Given Probability Youtube
Same probability is the same for the 12 As explained in the baccarat question, if the probability of something is p, then fair odds are (1/p)1 to 1 In this case fair odds would be 6 to 1 and a is the actual odds In Crapless Craps the place bet on the 2 and 12 pays 11 to 2 Using this formula, the house edge on the 2 and 12 is (655Equally, backing something at short odds with a potentially high probability does not guarantee it will become true As we have suggested, bookmakers use odds to display the probability or otherwise of all outcomes on sporting events They can do this in one of three ways fractional eg 2/1, decimal eg 300 or American eg 0To calculate implied probability, use the following formulas For negative numbers (favorites), drop the minus sign, then do Negative Odds / (Negative Odds 100) * 100 For positive numbers (underdogs) 100 / (Positive Odds 100) * 100




What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science




A Worked Example Calculating The Pretest And Post Test Probabilities Of Download Scientific Diagram
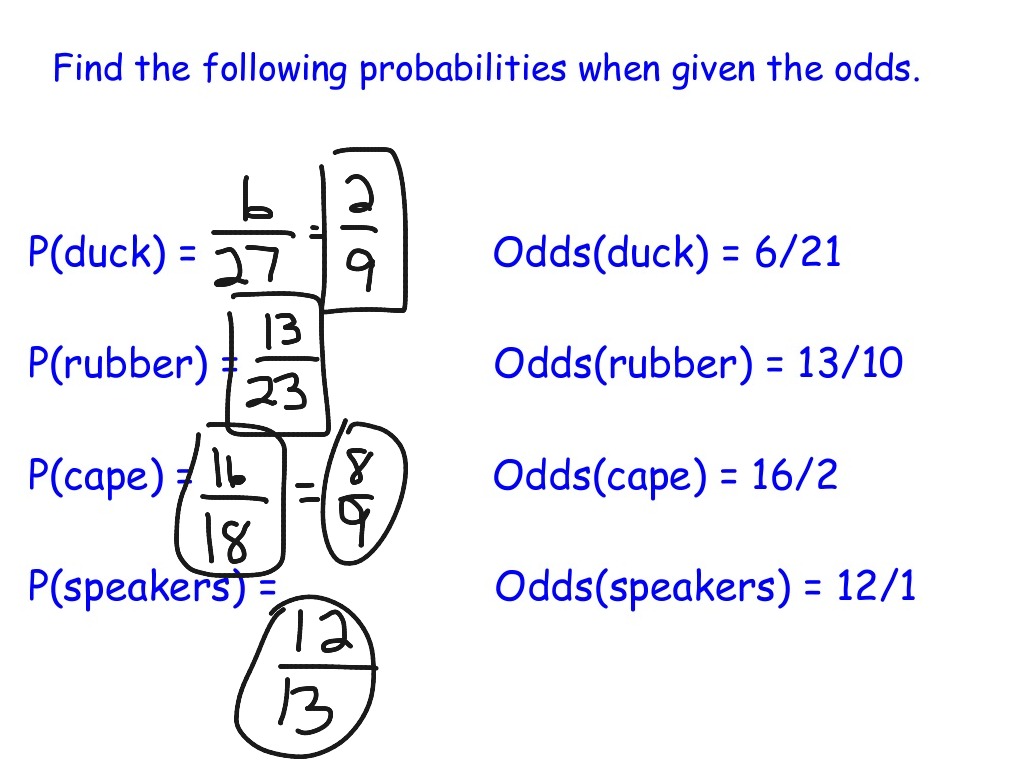
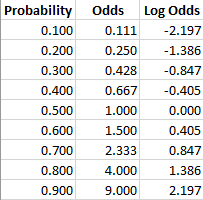
For converting odds to probability, we have to divide the odds by 1 odds For instance, let's convert odds of 1/9 to a probability Now, divide 1/9 by 10/9 to get the probability2 days ago To calculate the odds in favor, simply divide the one possible desired outcome by the total outcomes possible 1/6 = X 100 = 1667% chance of winning Conversely, the odds against our win can be solved the same way 5/6 Converting between odds and probability is straightforward To convert from a probability to odds, divide the probability by one minus that probability So if the probability is 10% or 010, then the odds are 01/09 or '1 to 9' or 0111 To convert from odds to a probability, divide the odds by one plus the odds



2 Odds Ghci Grade 12 Mathematics Of Data Management




How To Calculate Odds 11 Steps With Pictures Wikihow
To convert odds to probability, take the player's chance of winning, use it as the numerator and divide by the total number of chances, both winning and losing For example, if the odds are 4 to 1, the probability equals 1 / (1 4) = 1/5 or % Odds of 1 to 1 (50%) are called "evens," and a payout of 1 to 1 is called "even money"The interpretation of an odds is more complicated than for a risk The simplest way to ensure that the interpretation is correct is to first convert the odds into a risk For example, when the odds are 110, or 01, one person will have the event for every 10 who do not, and, using the formula, the risk of the event is 01/(101) = 0091Money Line Implied Probability The following chart shows how likely a team is to win based off the odds This is helpful in handicapping because you can see just what percentage of your wagers you need to win at each given money line in order to profit The left chart is to be used for favorites, the right for underdogs




Calculation Of The Post Test Probability Using The Likelihood Ratio Of Download Scientific Diagram




What Is Predicted Probability Magoosh Statistics Blog
Pretest probability and posttest probability (alternatively spelled pretest and posttest probability) are the probabilities of the presence of a condition (such as a disease) before and after a diagnostic test, respectively Posttest probability, in turn, can be positive or negative, depending on whether the test falls out as a positive test or a negative test, respectivelyHow to find probability and odds and the difference between the two We also discuss experimental probablility, theoretical probability, odds in favor, andMeaning Odds refers to the chances in favor of the event to the chances against it Probability refers to the likelihood of occurrence of an event Expressed in Ratio Percent or decimal Lies between 0 to ∞ 0 to 1 Formula Occurrence/Nonoccurrence Occurrence/Whole




Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To



Naive Bayesian
PostTest Odds = (PreTest Odds) x (Positive Likelihood Ratio) = 04 * 733 = 293 Conclusion Given a positive test, the PostTest Odds of having the disease is 293How To Convert Decimal Odds To Probability "Decimal Odds" are a simple reflection of the return you will receive for each single unit placed For example, let's say bookmaker Matchbook is offering odds of 165 for Manchester United to win This means that for every 100 you bet on that particular outcome, you will receive a profit of 065 The Difference Between "Probability" and "Odds" If a race horse runs 100 races and wins 25 times and loses the other 75 times, the probability of winning is 25/100 = 0 If the horse runs 100 races and wins 5 and loses the other 95 times, the probability of winning is 005 or 5%, and the If the



Why Do High Odds Mean A Low Chance Quora




Odds Ratios The Odd One Out Stats By Slough
These odds suggest that if this fight happened 21 times (8 13), Golovkin would lose 8 bouts and win 13 To calculate the implied probability of Golovkin winning the fight, take the number of times he is expected to win (13) and divide it by the total number of trials (21) This results in a 619% chance Golovkin will win the fightB = Decimal odds 1 P = The probability of winning Q = The probability of losing, which is 1 – p Following this formula allows you to master the Kelly bets This basically tells you the amount you should be betting, based on the true odds and the given odds, considering that the odds are not true Learn more about Bankroll Builder techniques Author King Yao, in his Weighing the Odds in Sports Betting, does an excellent job at outlining the formula for converting probabilities into money lines and viceversa Converting Estimated Win




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training




Odds




Converting Between Probability And Odds Mathwoes Youtube




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




What Are Implied Odds How To Use Implied Odds Like A Veteran Pro Upswing Poker



1




Converting Probability To Odds Example Youtube



Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsterm




Probability And Odds Youtube




Odds Ratio Sage Research Methods




The Odds Against A Solving A Certain Problem Are 4 To 3 And The Odds In Favour Of Solving The Same Problem Are 7 To 5 Find The Probability That The Pr




Learn Odds In Favour And Odds Against In 3 Minutes




Ppt Probability Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Probability Odds Odds Ratio Youtube




Odds Wikipedia




Section 11 6 Odds And Expectation Math In Our World Ppt Download




How To Calculate Odds 11 Steps With Pictures Wikihow



Log Odds Definition And Worked Statistics Problems




Odds Ratio Sage Research Methods




Probability Vs Odds In Favour Or Against An Event Examples Youtube



Our Calculations Explained Cancer Research Uk




Odds And Probability
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_The_Math_Behind_Betting_Odds_and_Gambling_Nov_2020-01-735accb453c8424b9e063c2c14e4edf4.jpg)



The Math Behind Betting Odds Gambling




What Are Implied Odds How To Calculate Implied Probability




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Learn Odds In Favour And Odds Against In 3 Minutes




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Calculating The Odds Of An Event Mathematics For The Liberal Arts




Odds Ratio Article




Scielo Brasil What Is The Probability Of A Patient Presenting A Pleural Effusion Due To Tuberculosis What Is The Probability Of A Patient Presenting A Pleural Effusion Due To Tuberculosis
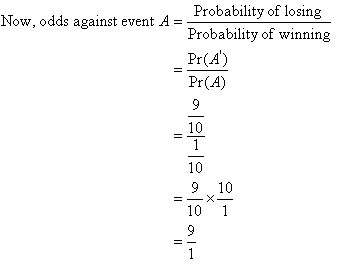



Odds




Logistic Regression In Python Blog By Cory Maklin



Probability Vs Odds What S The Difference Learn It And By Z Ai Towards Data Science




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Section 11 6 Odds And Expectation Math In Our World Ppt Download




Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio Is Used To Find The By Analyttica Datalab Medium




Difference Between Odds And Probability With Comparison Chart Key Differences
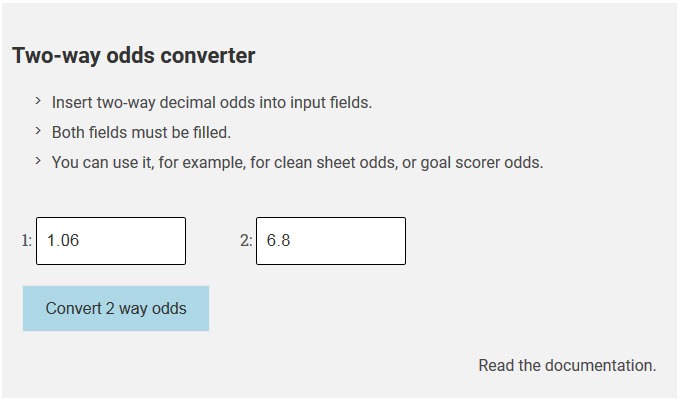



True Odds Calculator Find Probabilities Fair Odds Margin
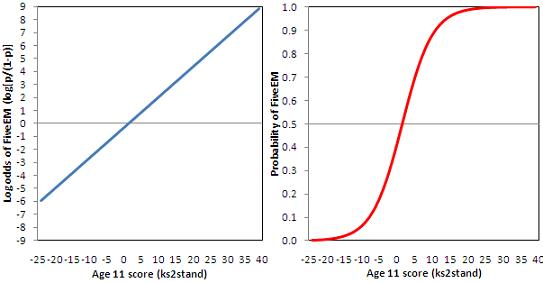



4 5 Interpreting Logistic Equations




A Worked Example Calculating The Pretest And Post Test Probabilities Of Download Scientific Diagram




Learn Odds In Favour And Odds Against In 3 Minutes
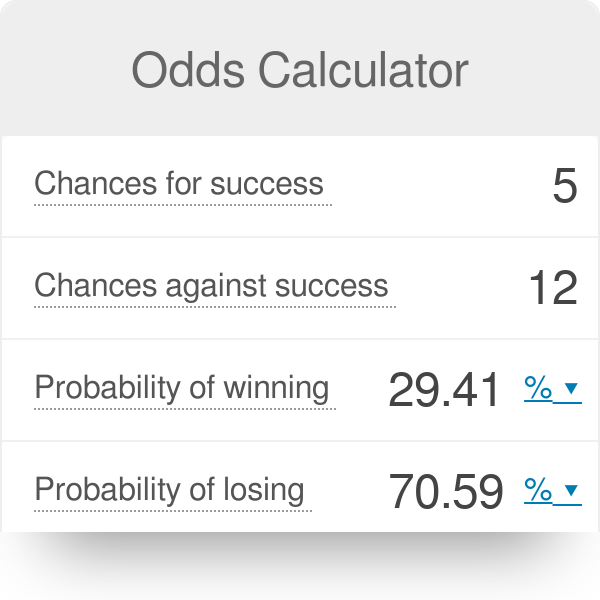



Odds Calculator




R Calculate And Interpret Odds Ratio In Logistic Regression Newbedev



1




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal
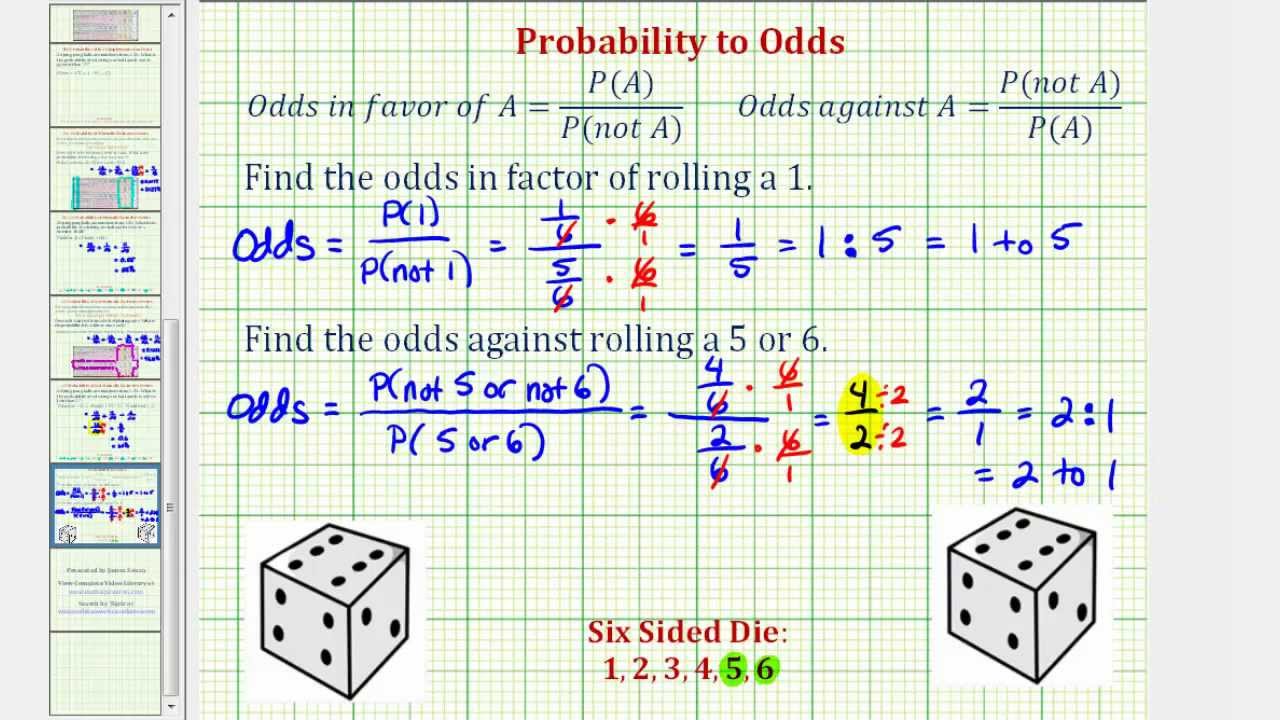



Calculating The Odds Of An Event Mathematics For The Liberal Arts
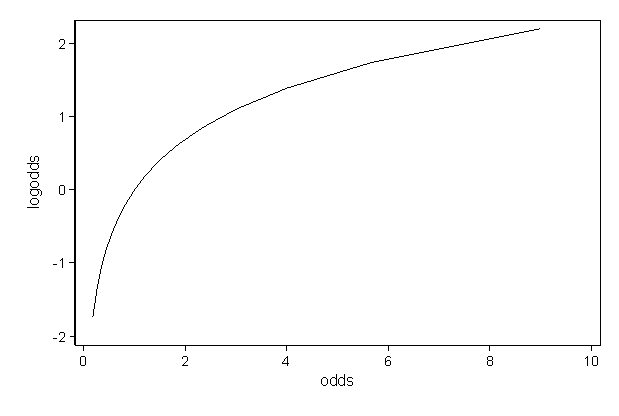



Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression
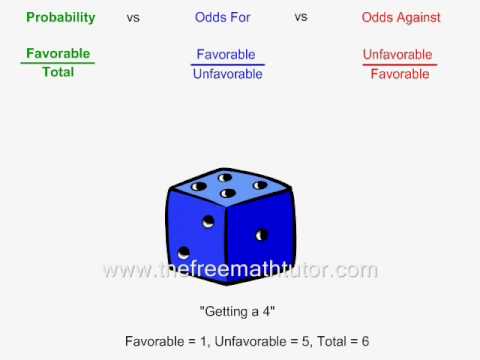



Comparing Probability Odds For And Odds Against Youtube
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/expected-5733972a5f9b58723d773687.png)



How Odds Are Related To Probability



Q Tbn And9gctef4moft93yz6f5nkwlt9 3oavpxscvjniheutpevbealx4t39 Usqp Cau




Formula Software For Statistics Mathematics Probability




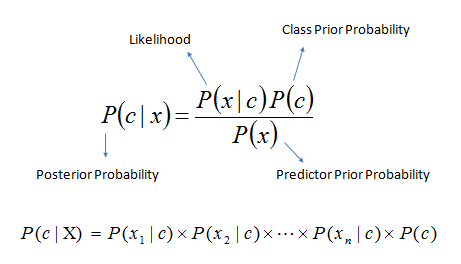
Bayes Theorem Is Used To Calculate The Probability Of An Outcome




Learn Odds In Favour And Odds Against In 3 Minutes




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Calculating Probability Of Dealer Busting S17 In Blackjack Stack Overflow



If The Odds In Favor Of An Event A Are 5 3 What Is The Probability Of Event A Quora
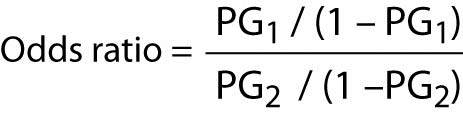



The Odds Ratio Calculation Usage And Interpretation Biochemia Medica
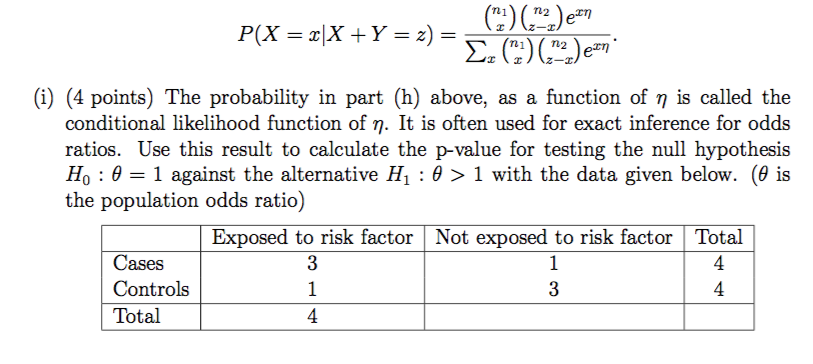



I 4 Points The Probability In Part H Above As Chegg Com



Q Tbn And9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau



Stats What Does A 60 Drop Mean June 05




Logistic Regression Calculating A Probability




How To Calculate Odds 11 Steps With Pictures Wikihow




What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science
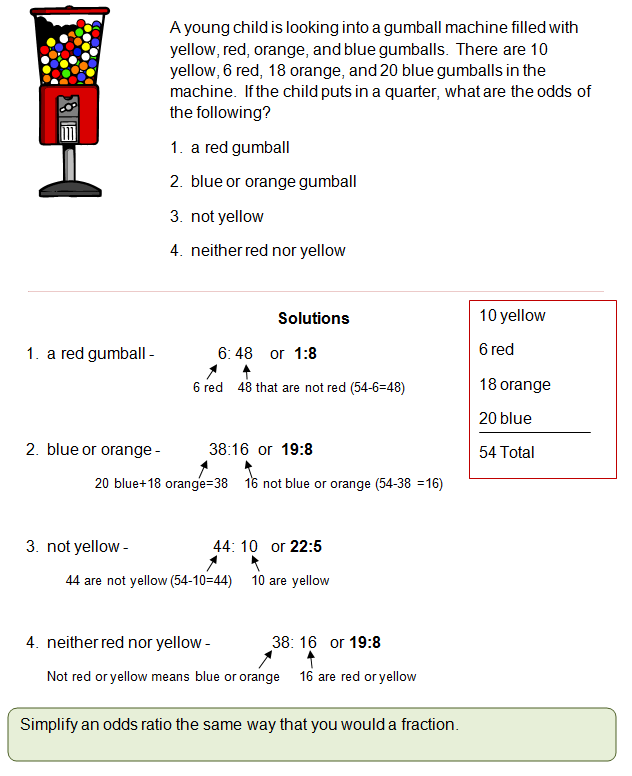



Odds And Probability




Odds In Favour Of An Event Is 2 3 Find The Probability Of Happen




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research




9 Calculate The Odds For And Odds Against Winning Chegg Com



Logistic Regression




Section 11 6 Odds And Expectation Math In Our World Ppt Download




Logistic Regression A Concise Technical Overview Kdnuggets




Introduction To Probabilities Farrokh Alemi Ph D Saturday



Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsterm



The Difference Between Probability And Odds



2 Odds Ghci Grade 12 Mathematics Of Data Management



2 Odds Ghci Grade 12 Mathematics Of Data Management



Odds Likelihood Ratios Guide To Diagnostic Tests




Webmining Agents Probabilistic Information Retrieval Prof Dr Ralf
/JointProbabilityDefinition2-fb8b207be3164845b0d8706fe9c73b01.png)



Joint Probability Definition




How To Calculate Odds 11 Steps With Pictures Wikihow



Probability Odds Lessons Blendspace



Logistic Regression From Bayes Theorem Count Bayesie
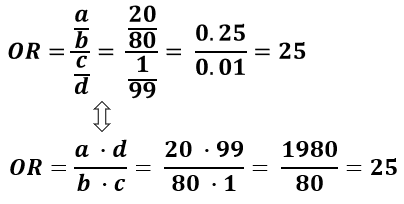



Odds Ratio Calculator Calculate Odds Ratio Confidence Intervals P Values For Odds Ratios



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿